BREXIT – What it means
It is a well-known fact and one of the most discussed topics universally,UK has decided to exit EU by 31st October 2019. 52% of Votes in favor of exit from EU.
EU was formed post WWII to for ease of trade and peace among nations. EU is a union of 28 countries inclusive of UK of which 19 countries use the euro as their official currency. The purpose to form EU was to allow people, goods, services, and capital to move freely between member countries. All these countries act as one economic unit in the world economy and follow laws and values determined by the European Union.
Why does UK want to exit?
Post 2008 financial crisis Portugal, Ireland, Greece, and Spain have been struggling to recover. Greece and Ireland received financial bailouts from the community in 2009, Portugal followed in 2011, along with a second Greek bailout. Problem remained stagnant. Countries with stable economy such as Germany, UK and Netherlands begrudge the financial drain.
Another reason for Brexit was huge increase in immigration into Britain for job opportunities from the struggling countries which leads to competition and reduces the opportunities for residents.
People were afraid of an increase in refugees. They felt that EU membership was changing their national identity. Britain was mostly against the majority of the policies imposed by EU.
Impact of Brexit on Euro
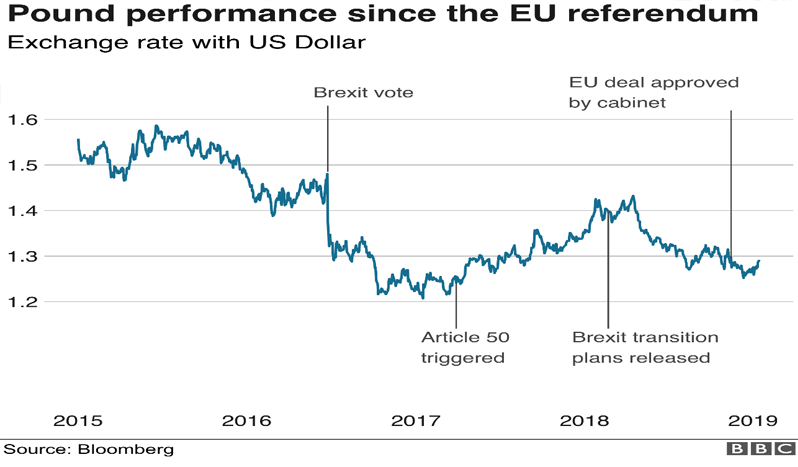
As of now no terms or deals are finalized between UK and EU regarding their divorce which is well known as Brexit. At this stage following options are on the table regarding Brexit.
Hard Brexit
The UK would leave not only the EU but also the EU’s Single Market (of which non-EU countries are also members) and the EU Customs Union (of which non-EU countries are also members) which means there won’t be free flow of people, goods, services, and capital between EU and UK. It is quite likely that UK would have to trade with the EU and other countries under World Trade Organization rules. This is expected to have a negative impact on the UK economy.
This means they would set up their own independent trade agreements with other countries.
Moreover, imported goods will suddenly become much more expensive, and impact importers business adversely. Currently, approximately 45% of the U.K.’s exports are to the EU while 50% of the goods it imports come from the EU.
No Deal
Unlike, a hard Brexit, which could include some sort of agreement with the EU and potentially set out a deal where the UK have some sort of silver lining.
Consequences of no deal scenario are not in favor of Britain. In no deal scenario UK may reconsider Brexit.
Soft Brexit
Soft Brexit is the least damaging path. In soft Brexit to Britain remaining closely aligned to the EU by retaining some form of the bloc’s single market. This scenario would minimize disruption to trade, supply chains and businesses in general.
However, the EU has demanded that access to the single market and only be granted if all its principles, including the free movement of people, are respected. UK isn’t willing to compromise on immigration, claiming that such a deal would betray the wishes of the British public.
References
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/europeanunion.asphttps://www.investopedia.com/hard-soft-on-hold-or-no-deal-brexit-outcomes-explained-4584439
https://www.bbc.com/news/business-46862790

