One of the biggest reasons adjudged behind 2008 financial crises was Inadequacy of Information technology (IT) and Data Architectures. A vast majority of Banks lacked the ability to aggregate risk exposures and manages their risks appropriately.
To overcome from these inadequacies, Standard 239 by Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) launched in January 2013. BCBS 239 is a set of principles aimed at strengthening banks, governance frameworks, risk data aggregation capabilities and internal risk reporting practices.
There are 14 Principles in BCBS 239. These 14 principles are later sub categorized under four sections:
- Overarching governance and infrastructure
- Risk data aggregation capabilities
- Risk reporting practices
- Supervisory review, tools and cooperation
A. Overarching governance and infrastructure
Principle 1 – Governance:
A bank’s data aggregation capabilities and risk reporting practices should inclined with the principles and guidance provided by the Basel Committee.
Principle 2 – Data Architecture and IT infrastructure:
Bank should maintain accuracy in risk data aggregation and effective IT support in spite of any limitations
B. Risk data aggregation capabilities
Principle 3 – Accuracy and Integrity:
The capacity to generate authentic and reliable risk data, so at the time of crises it projects a clear image of the scenario. Also, data aggregation process should be automated as much as possible to minimize the errors.
Principle 4 – Completeness:
Capacity to generate correct and complete risk data.
Principle 5 – Timeliness:
Data is complete and accurate but its unavailable at the time of need might lead to another financial crisis.
Principle 6 – Adaptability:
The process of data aggregation must be flexible and customizable. It should be designed to incorporate new developments and changes in the regulatory framework.
C. Risk reporting practices
Principle 7 – Accuracy:
Risk management reports should be accurate and reliable so that the management can rely on it and make critical decisions.
Principle 8 – Comprehensiveness:
Reports must include all sort of information about risk data that is relevant to the bank for decision making.
Principle 9 – Clarity and Usefulness:
Reports must be easy to understand without compromising comprehensiveness. It includes data analysis and interpretation, and qualitative explanations.
Principle 10 – Frequency:
Management should set the frequency of risk management report production and distribution, so the needs of organization are met.
Principle 11 – Distribution:
Reports should be distributed to the concerned people only to maintain the confidentiality. Reports can be tailored as per the requirement of receiver.
D. Supervisory review, tools and cooperation
Principle 12 – Review:
Management should timely review whether the above principles are being implemented effectively.
Principle 13 – Remedial actions and supervisory measures:
Management must have right tools or measures to overcome from its inadequacies.
Principle 14 – Home / Host cooperation:
Management should cooperate with relevant supervisors in other jurisdictions regarding the supervision and review of the Principles, and the implementation of any remedial action if necessary.
Challenges in Implementation of BCBS 239
BCBS 239 impacts the entire structure of enterprise.
Most of the banks lack required IT infrastructure for aggregation of risk data
Unclear structure of data governance
Manual aggregation of risk data
Irregular generation of reports
Inability in identifying who owns what data.
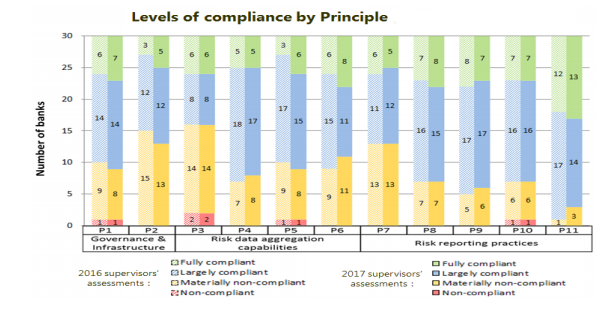
BCBS 239 – Assessment
In 2013-15, the Committee introduced 3 reports based on self-assessment by banks on their progress towards compliance with the Principles. In March-2017, a comparison progress report was published for 2016 and 2017 towards implementing of principles. The aim of this report is to identify the key deficiencies and suggest key recommendations to promote principles implementation.
Below are the recommendations, the report including:
Banks should create a clear roadmap to attain full compliance with principles.
Supervisors should communicate with banks for their supervisory assessment and provide incentives for full compliance with principles.
Continue to cleanse their approaches.
Impact of BCBS 239
Effective decision making through better data aggregation and data governance
Reduce counter party risk through the accurate and comprehensive reporting structure made under BCBS 239
Advance IT and Infrastructure will help in growth of organization
Transparency increases through continuously monitor and review
Improves organization strategic planning
Prepares for future changes
Helps in tackling future crises/stress situation and surviving them
Prevents any financial crises in future
Improve Data quality
For ref visit following links:
https://www.bis.org/bcbs/publ/d443.pdfhttps://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs239.pdf

